Wetlands 4 Resilience
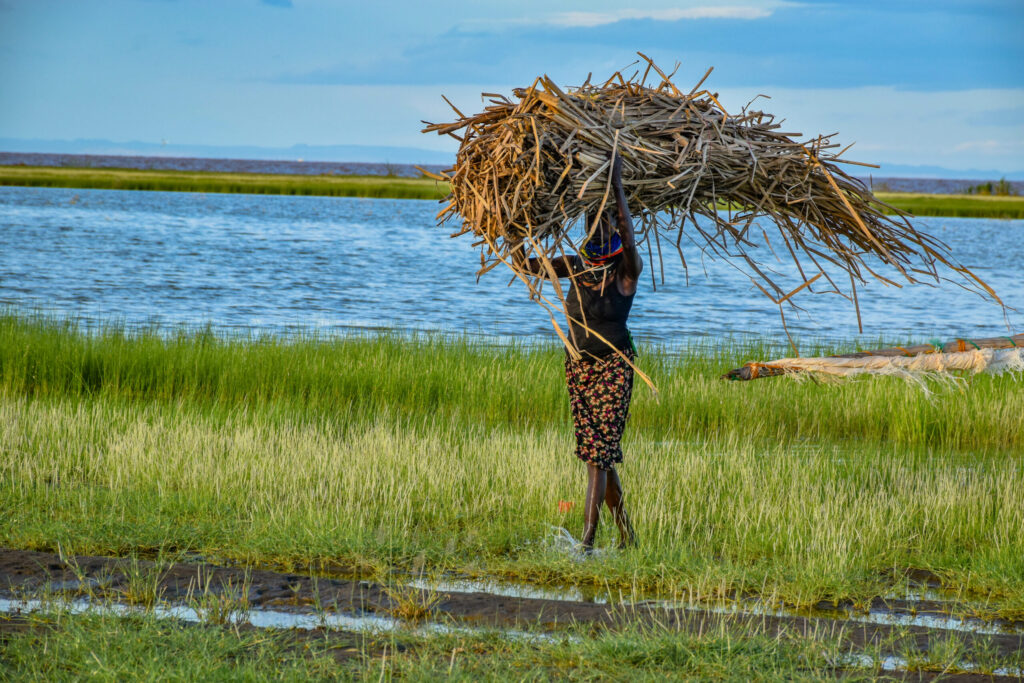
Healthy wetlands underpin our societies and economies, sustain countless species and ecosystems, and are critical to a stable climate. They provide us with water, food and medicines. They protect cities and communities from floods, droughts and storms. Wetlands directly support the livelihoods of a billion people as well as extraordinarily rich biodiversity. Mangroves and peatlands store vast amounts of carbon and are central to efforts to adapt to the worsening impacts of climate change, reduce disaster risk and build longer term resilience.
From rivers to reefs, peatlands to ponds, and marshes to mangroves, healthy wetlands are essential for people, nature and climate. But we are losing these valuable ecosystems.
We urgently need to scale up investment in protecting, restoring and sustainably managing wetlands, including redirecting financing and shifting incentives away from destructive activities and towards investments that enhance wetlands.
The Wetlands 4 Resilience (W4R) programme, developed with support of the Swedish International Development Cooperation Agency (Sida) addresses this urgent need aiming to upscale wetland restoration in target countries and globally contributing to climate-resilient sustainable development.
W4R objectives
- Share learnings and methodologies for holistic, ecosystem-led resilience building, from our global wetland landscape portfolio and partner programmes;
- Design and apply a Wetlands 4 Resilience model approach, toolkit and guidance to accelerate upscaling in our major wetland landscape regeneration programmes;
- Catalyse wetland landscape regeneration by others, through uptake and implementation of the W4R model approach across different sectors, globally.
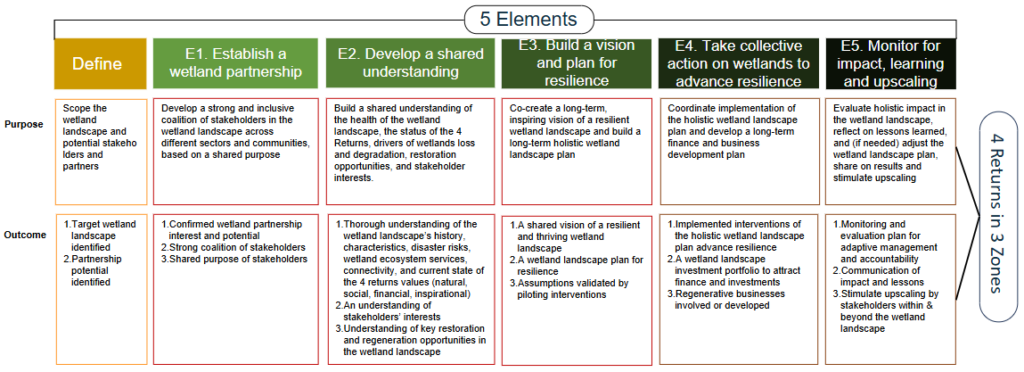
The W4R Model Approach
The W4R Model Approach describes a process specifically tailored for holistic wetland landscape restoration. It consists of five key Elements, each defined by its primary purpose and intended outcomes. By applying this model approach stakeholders can work toward natural, social, financial and inspirational returns delivering resilience across natural, economic and mixed zones in wetland landscapes. Through the W4R programme we will also develop a Toolbox, and build capacity on how to use it in practice, using W4R landscape cases to showcase best practice interventions and results that can be achieved. The expected outcome is that additional landscapes will apply W4R approaches and practices and contribute to upscaling of wetland restoration and positive impact beyond W4R target landscapes.
The W4R Program
The Wetlands 4 Resilience programme works both at the global level actions in specific target landscapes.
At the global level we will develop a W4R Model Approach & Toolbox, share and build capacity on how to use these in practice, and through regional and global awareness -using W4R landscape cases- stimulate wetland restoration by other stakeholders.
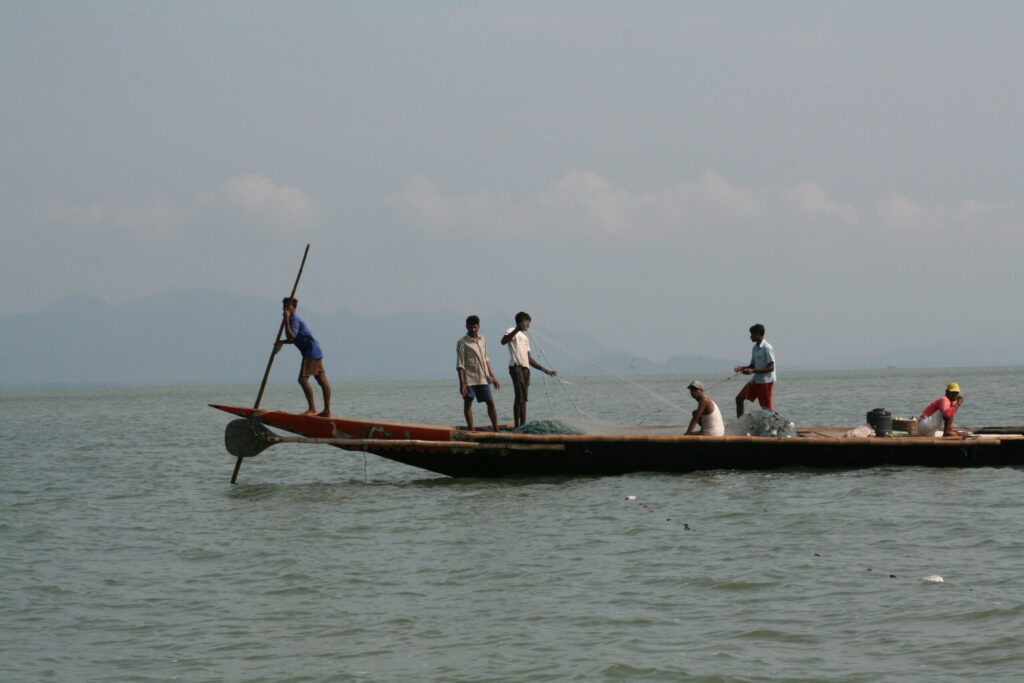
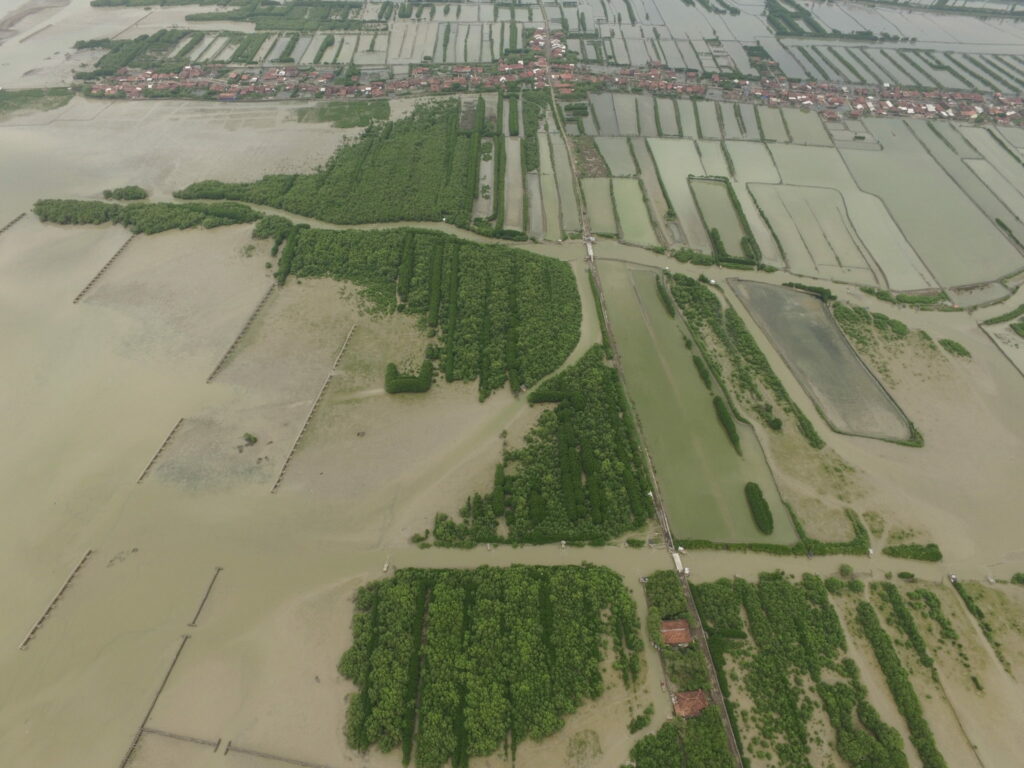
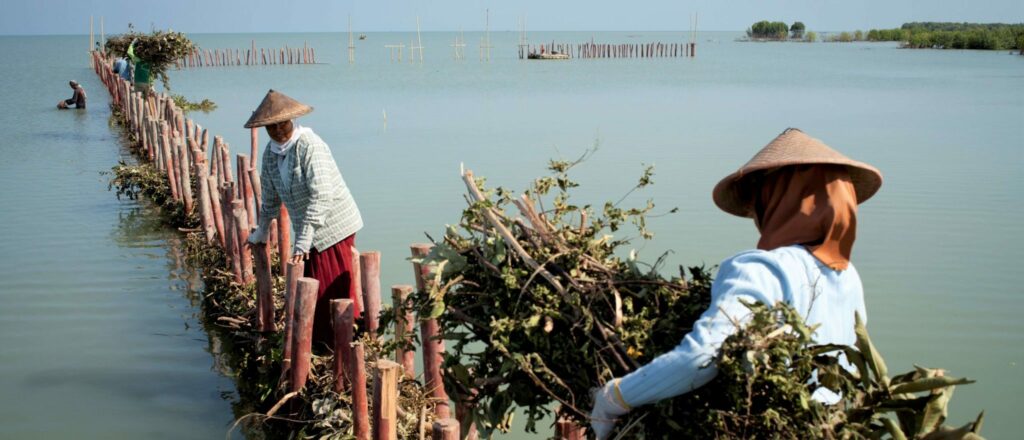
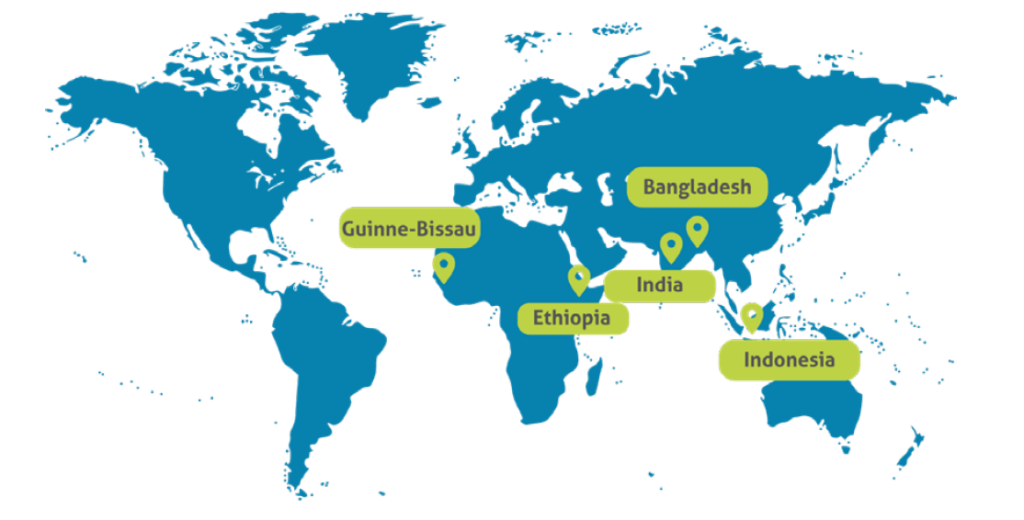
At the landscape level, W4R is being implemented in the Sundarbans in Bangladesh, the Ziway-Shalla sub-basin in Ethiopia, and in Jeta-Pecixe-Cacheu in Guinea-Bissau. Furthermore, lessons are captured and shared from the landscapes in Demak, North coast of Java in Indonesia, and Mahanadi delta in India, two landscapes where Wetlands International has been involved in for over 2 decades and where landscape scale action has been reached. In Bangladesh, we are supporting a functioning W4R Landscape Partnership that will assess the Sundarbans wetlands and climate resilience context, define an Engagement Strategy and start dialogues. The aim is for there to be a jointly-owned plan to conserve and restore the Sundarbans landscape. In Ethiopia and in Guinea-Bissau, we are supporting Landscape Partnerships on adapted planning and policy processes and supporting the development of guidelines and management plans. Furthermore, through policy influencing and capacity building we are working on national policies and action plans supportive of wetlands to enhance climate-resilient sustainable development. We are working to implement best practice interventions to show the opportunities in the landscapes, and develop a Landscape Proposition and Investment Framework. The aim is for innovative and integrated collaborative planning to lead to increased investments and upscaling of wetland restoration to enhance climate-resilient sustainable development.
Achievements to date
Globally
In collaboration with other stakeholders, we developed a global guidance document on the integration of wetlands into National Biodiversity Strategies and Action Plans (NBSAPs), which was widely shared at the UNFCCC, CBD, and UNCCD COPs. Through participation and organization of several key sessions, W4R helped shape global policy narratives on nature-based solutions, elevating the role of wetlands in climate resilience and ecosystem restoration agendas, as visible by the Baku Declaration of the Water Dialogues at UNFCCC COP29 referring to the Freshwater Challenge (FWC), and the Riyadh Action Agenda launched at UNCCD COP16 prominently featuring the FWC.
Ethiopia
A Multi-Stakeholder Platform has been established in the Ziway-Shalla Sub-basin that fosters collaboration among diverse stakeholders, advancing integrated planning efforts in the landscape by working towards a shared vision.
In 2024, 886 members of community-based organisations (CBOs) committed to safeguarding 893 hectares of wetland ecosystems in the Ziway-Shalla sub-basin. This marks a significant shift toward community-led stewardship, helping reduce human and livestock encroachment while contributing to conservation and climate resilience. The W4R work in Ethiopia builds on previous work of Wetlands International and stakeholders in the sub-basin, and aims to support upscaling of these efforts through supporting the landscape partnership.
Guinea-Bissau
The JPC Landscape Stakeholders Platform to support sustainable development in the JPC wetlands landscape has been established and is operational.
In 2024, a participatory mapping process of an area over 447,000 hectares in the Cacheu region resulted in the formal submission of a cartographic package to national authorities as part of Guinea-Bissau’s application for UNESCO Biosphere Reserve status. This process strengthened regional spatial planning and governance by engaging local stakeholders in decision-making. In parallel, the Community Forest Model in Mata d’Uco was recognized as a best practice for collaborative natural resource management, with plans initiated for its replication in other areas.
Best practices in an Integrated Landscape Approach
Resources









